Like a skyscraper, the launch of Laravel application requires solid foundations to safely build additional floors (features). Over time, the Laravel ecosystem continues to expand and become complicated; what may have been considered a solid, durable structure during the last update now contains critical areas of weakness.
Experienced developers unintentionally fall behind in performance by creating slow queries and bloated controller logs. This guide consolidates the blueprint and outlines 10 Laravel tips from the industry experts on how to maximize your application’s speed, knowledge, security hardening, and support for future growth.
The expert information given in this blog will help you to create a cleaner code, speed up the time required to deploy a Laravel app, increase the level of security within your app, and stay ahead of the curve in an ever-changing environment where both efficiency and reliability are crucial.
Table Of Content
What is Laravel? Developer’s Edition
It provides a detailed overview of the Laravel Framework, which enables developers to create high-quality web applications with a clean architecture, excellent performance, and a beautiful syntax. It provides a variety of convenient and helpful built-in features for all aspects of development, including caching, routing, database migration, and authentication, among others, allowing developers to focus on producing high-quality code without being bogged down by repetitive tasks. Laravel offers a highly modularized structure along with its incredible built-in security capabilities and robust tooling, making it extremely desirable for a new developer to use.
From a developer’s standpoint, Laravel doesn’t just provide an extensive framework; it also offers developers an entire ecosystem for creating applications with the aid of tools such as Blade for templating, Eloquent ORM for interfacing with databases, Laravel Mix/Vite for compiling and serving assets, and the command-line interface (CLI) tool Artisan for automating tasks. By employing these tools together, developers can create applications that are easier and quicker to develop while being simple to scale.
In terms of deployment, reliable Laravel hosting solutions provide an optimized environment specifically to take advantage of the speed. With high speed, Artisan commands run smoothly, there’s an ease of management of queued jobs, automated backups, and adequate resources for serving applications experiencing heavy loads. Developers can push code to the server with complete confidence by choosing a Laravel-friendly hosting provider.
While it seems like a “nice-to-have” to optimize Laravel application performance, users will expect instantaneous responses when working with any application. Therefore, using the techniques mentioned above will provide developers with cleaner and lighter code that results in significantly faster applications running on their servers.
10 Expert Laravel Tips Every Developer Should Know
Laravel applications that perform well don’t just appear by chance. Creating high-performance applications with Laravel requires good coding practice and an optimized architecture combined with careful understanding of its most powerful features. The following expert tips will help developers create cleaner code, improve performance, secure applications, and create scalable applications.
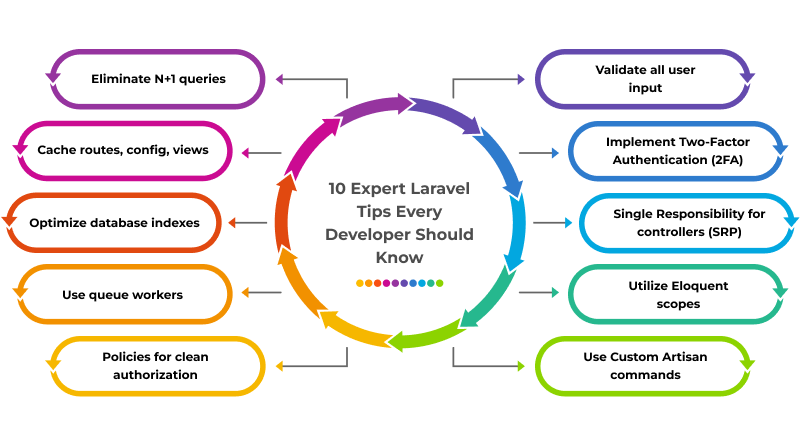
Tip No. 1: Leverage Eager Loading (Solve the N+1 Problem)
The best practice is to always load relationships with either
`with()`or `load()`
when working with related models.
- Why it’s beneficial:
When you don’t use eager loading, each relation will trigger a separate query. For example, if you had to create a webpage that shows 100 users, each with their own collection of posts, this would become 101+ separate database queries. By using eager loading, all of those queries can be combined into 2.
- Example:
- php: $users = User::with(‘posts’)->get();
- php: with([‘posts.comments’, ‘roles.permissions’])
- php: User::with([‘posts’ => fn($q) => $q->published()])->get();
- Tools/Best practices:
- Laravel Debugbar: Instantly identifies N+1 queries.
- Laravel Telescope: Good for detecting heavy query patterns.
Tip No. 2: Cache Everything Possible (Routes, Configurations, Views, Queries)
The best practice is to cache anything that doesn’t need to be recalculated for every request.
- Production commands that are meaningful:
- `php artisan route:cache`
- `php artisan config:cache`
- `php artisan view:cache`- Why it’s beneficial:
It avoids the cost of parsing large numbers of files and speeds up your response time drastically.
- Power Moves:
– Cache costly queries like:
php: Cache::remember('top_products', 3600, fn() => Product::popular()->get());Use Redis as a caching system rather than file-based caching when building larger applications. Cache responses from third-party APIs so your application can handle temporary downtime of external systems.
- Tools/Best practices:
- Monitoring tools for Redis queues and caching loads with Laravel Horizon
- Cache entire Laravel responses with Spatie Laravel ResponseCache.
Tip No. 3: Optimize Database Indexes
To optimize database indexes, always create indexes on all columns used in any query via a WHERE clause, ORDER BY clause, JOIN clause, and all foreign key columns.
- Why it’s beneficial:
Indexes make it possible for your database engine to find data without having to scan the entire table. If your database contains many records, the absence of an index will be a significant error.
- Example:
Schema::table('orders', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->index('user_id');
$table->index('status');
});
- Additional Tips:
Whenever you are frequently combining multiple columns together in a query, consider creating composite indexes. Indexing small tables is usually not helpful and sometimes can decrease the insertion speed of new records.
Use these tools to analyze your slow queries:
- mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT …
- Laravel Telescope’s ‘queries’ panel helps to analyze slow queries.
- Tools/Best practices:
Make it easier to manage the index audit process with the Percona toolkit.
Visualize slow queries by using MySQL Workbench.
Tip No. 4. Use Queue Workers (Your Asynchronous Secret Weapon)
Moving tasks that are not essential to completing the request process out of the request cycle helps to make the application responsive for users.
- Examples:
- Sending an email to customers
- Sending notifications to customers
- Processing Images and Video Files
- Making requests to third-party APIs
- Generating reports
- Why it’s beneficial:
Queues Keep your application responsive by delegating work to background workers in real-time, allowing background workers to perform heavy lifting without disrupting a user’s experience with the app.
- Basic examples:
SendWelcomeEmail::dispatch($user)
Scale up queue workers with a daemonized PHP process run by using:
php artisan queue:work --daemon- Tools/Best practices:
Laravel Horizon: Advanced queue monitoring.
Supervisor: Ensures workers remain operational during failures.
Tip No. 5: Laravel Policies for Authorisation
When it comes to security, Laravel stands above the rest. Nevertheless, only if developers correctly use its features. Security threats in the form of credential stuffing, API abuse, and automated attacks are becoming increasingly frequent.
The objective here is clearly to “tighten” your application so that nothing slips through the cracks. The authorization logic should not be located within controllers anymore. Using policies provides for a cleaner, scalable, and easily auditable application. You can generate a policy with the following command:
php artisan make:policy PostPolicy --model=Post- Why it’s beneficial:
Instead of having permission checks scattered throughout your application, the logic is now centralized and organized. This reduces the risk for accidental privilege leakage as your application grows.
- Tools/Best practices:
Use Gates for basic checks.
Use policies for resource-based permissions.
Add @can directives in your Blade files or authorize() in your controllers.
Utilize Laravel’s built-in testing helpers to test your permissions.
- Extra:
Policies work beautifully with Laratrust, Spatie Roles and Permissions, and Bouncer for substantial RBAC.
Tip No. 6: Validate All Input
Every form, API call, or background request is a potential attack vector, and validation is your first line of defense and security. Move the authenticated user validation logic to the Form Request classes by executing the command:
php artisan make:request StoreUserRequest- Why it’s beneficial:
By using validation logic to filter maliciously submitted data, you protect your application from the following:
- SQL Injection
- XSS (Cross-site Scripting)
- Malformed Data
- Unpermitted File Upload
- Tools/Best practices:
- Use the sanitize() method or custom rules to cleanse input before storing it.
- When validating input for JSON APIs, validate using the validate() method or use Form Request classes.
- Use the bail rule to stop checking further rules once a first failed validation rule is hit.
- When validating file uploads, use the MIME types and file validation rules.
- When validating data against a database, use the existing and unique validation rules.
- Extra:
Enable Laravel’s HTML Purifier for automatically cleaning input for rich text editor fields.
Tip No. 7: Strengthen with 2FA
Using only a password is no longer secure. Adding an additional layer helps keep admin accounts and other sensitive dashboards secure.
- For implementing 2FA, you can use:
- Laravel Fortify: An official package from Laravel.
- Laravel Breeze plus Simple TOTP packages.
- Google Authenticator integrations.
Similar Read: Top 10+ Laravel Admin & Website Templates for Developers
- Why it’s beneficial:
- 2FA protects against the following:
- Credential stuffing
- Stolen passwords
- Bot attacks
- Exploited sessions
- Tools/Best practices:
- For secure API authentication, use Laravel Sanctum.
- Set the session lives to appropriate times (SESSION_LIFETIME)
- Implement log-in throttling using Laravel’s built-in rate limiting feature.
- Use HTTPS with HSTS headers for secure connections.
- Enable security middleware such as EncryptCookies.
- Extra:
For enterprise-level applications, you may want to consider integrating:
- WebAuthn (FIDO2)
- Passkeys
Extra Security Measures
- Make distinct configurations for each environment
Don’t put API keys or secrets directly in a codebase (this includes hardcoding any other credentials there). Use a .env file to store them instead and rotate your credentials frequently.
- Secure Important Routes
Use middleware such as auth, verification, and password. Confirm or develop your own middleware for custom roles.
- Secure Uploaded Files
Validate both the file extension and the MIME type of uploaded files. Don’t store uploaded files in the /public directory unless strictly necessary.
- Enable Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) Protection
CSRF protection for forms is automatically set by Laravel, but it is important that API calls have the appropriate CSRF token or use Sanctum.
- Enable Rate Limiting in Laravel
Limit the number of requests to APIs by enabling the rate-limiting feature, e.g.,
RateLimiter::for('api', function () {
return Limit::perMinute(60);
});- Logging Everything
- Log everything using Laravel’s log channel feature, possibly in conjunction with something like:
- Sentry, Papertrail, and Bugsnag.
- Audit trails can assist you in determining if something bad is happening before it happens.
Clean Code & Best Practices
The single best clue that your code is well organized and has the potential to last for years is clean code. The goal behind clean code is simple – code that is easy to read, easy to test and easy to change. This document provides the best practices to develop a clean code.
Tip No. 8: Implement Single Responsibility Principle in Controllers
Keep your controllers slim. If your controller method exceeds 20–30 lines, it indicates that the controller should contain nothing but controller methods and that the logic contained therein could be removed and placed into a service class, an action class or a job.
- Why it’s beneficial:
Cleaner controllers will make your code readable and easier to test for each of your classes. As a result, you will have a much more scalable system, i.e., easier to update and maintain over time.
- Additional Tips
While it is a good practice to implement a clean controller methodology, it is not recommended to have a controller become overloaded with business logic, and therefore models should be used for business logic instead. The repetitive logic should be shared between services or actions.
- Tools/Best practices:
- Utilize the Laravel Actions Package.
- Utilize Laravel Service Classes, which are located inside of the app/Services folder.
- Utilize Form Requests, which can be used to automatically validate and sanitize user input.
Tip No. 9: Utilization of Eloquent Scopes
Use local scopes to contain commonly used query logic. If you find yourself having to write the same query condition multiple times, then that logic should be put inside a scope.
- Example:
public function scopeActive($query) {
return $query->where('status', 'active');
}- Why it’s beneficial:
Using Eloquent Scopes keeps controllers clean by making the queries more expressive and avoids errors from logic being repeated in multiple places.
Further Tip: Utilize global scopes for soft deletes, multi-tenant filters, or automatic ordering as required.
- Tools/Best practices:
- Eloquent Scopes
- Laravel IDE Helper for autocomplete.
Tip No. 10: Utilize Custom Artisan Commands
All scheduled tasks, cleaning routines, importing data via scheduled imports, and administrative utilities should be created as custom artisan commands using the following command:
php artisan make:command CleanOldRecords- Why it’s beneficial:
It organizes your recurring jobs, makes them easier to test and reuse, and seamlessly integrates with Laravel Scheduler, so you can automate your scheduled routine. You can add logging inside your commands so you always know what commands have run and what commands have failed in production.
- Tools/Best practices:
- You use Laravel Scheduler.
- You may use Horizon if your command triggers queues.
- You can use Telescope if you need to debug.
To become a master Laravel developer, you need to find the right balance between speed, security, and beauty. Because of its beautiful, expressive syntax, internal tools, and modular architecture, you can create maintainable, high-performing applications.
If you know and understand Laravel’s marketable skills and apply them, you can always produce scalable, safe, and fast applications while enjoying the beauty and clean experience your framework offers.
FAQs
1. What are some must-know Laravel tips for beginners?
For beginners, the most important thing is to understand the basic concepts of Laravel, like routing, controllers, middleware, and Eloquent ORM. Also, using Laravel’s Sail or Homestead for a consistent environment is very useful. Following the folder structure strictly and learning Blade templating very early simplifies the process of building clean applications. The best practice for beginners is to use Laravel’s internal tools rather than build the tools themselves, like Tinker, artisan commands, and validations.
2. How can Laravel development improve website performance?
Performance is improved via optimization features such as route caching, config caching, and optimized Eloquent relationships that eliminate redundant queries. Developers can utilize queue management systems in addition to caching systems at various layers, such as Redis or Memcached. Controlled asset loading is achievable via Laravel Mix or Vite.
3. What are the best Laravel practices for cleaner code?
Higher code cleanliness metrics can be achieved via resource controllers, form request classes that handle validation, dependency injection alongside Eloquent relationships, and several other best practices. Other best practices include adherence to the solid principles, logical code sectioning within varying service or repository layers, and utilization of standard naming conventions, as they ensure predictable behavior. Regular code maintenance and use of Laravel Pint can improve code quality and provide clear metrics.
4. How can I optimize Laravel performance for large-scale applications?
In giant systems, the focus should be on query optimization, table indexing, and reducing N+1 issues with eager loading. For background work, queues should be used, along with horizontal scaling with load balancers and caching at every level in the system. Laravel’s production readiness can be improved by deploying with Octane or by using Swoole/RoadRunner to improve throughput.
5. Are there any Laravel security tips to protect my application?
Laravel provides reasonable protection by default, but developers need to activate HTTPS, validate inputs properly, and update dependencies regularly. With useful features such as CSRF protection, password hashing, and scaffolding for authentication, Laravel offers a defense against various attacks. For web applications, mass assignment is avoided through guarded models, and user data is pre-validated. .env files need to be protected, as environment variables shouldn’t be public.
6. Which Laravel tips help speed up development time?
Artisan generators, pre-packed starter kits (like Breeze and Jetstream), and reusable features allow for rapid development. Eloquent relationships, form requests, and API resources help cut down on repetitive code. Developers are free to use resources in the Laravel ecosystem, automate by using Laravel Forge and Envoyer, and use Pint to help with formatting.
7. Why should developers follow Laravel best practices?
Best practices help ensure the Laravel applications are clean, scalable, secured, and ready for the future so the framework can continue evolving. With the newer AI-backed tools, better caching, and performance boosts with Octane, it will help disciplined coding be flexible to adapt to the projects. Best practices minimize technical debt, help in working with a team, and help with stability over time, which is important in production environments.