The field of information technology is always changing, and virtualization and hypervisor technologies are evolving alongside it. Virtual machines and hypervisors enable you to create and run multiple virtual environments to host applications on the same server. If you have deployed KVM technology, then KVM VPS server is the right choice for meeting operational needs. It is increasingly necessary for organizations that use servers to maximize resource use, scalability, and management effectiveness.
Two major virtualization technologies, KVM and ESXi, are common hypervisors in the IT sector. The guide highlights how these technologies have profoundly shaped the IT architecture of modern cloud computing environments.
Table Of Content
What is ESXi?
VMware ESXi is a widely adopted Type I hypervisor. It effectively manages resources in the enterprise environments with robust virtualization capabilities. It was developed by VMware. ESXi is directly installed on the physical server. It offers the foundation for the creation and management of virtual machines.
With VMware ESXi, administrators have the ability to create and manage different virtualized environments. A management tool, vSphere enables admins to control and monitor multiple ESXi servers through a centralized system. It permits CPU cycles, network bandwidth, and memory to be shared with the physical machine.
What is KVM?
KVM (Kernel Virtual Machine) is software that allows you to install on physical Linux servers to create virtual machines (VM). A virtual machine is an independent computer within another physical computer. It shares resources like CPU cycles, network bandwidth, and memory with the physical machine.
KVM has operated on Linux VPS servers since 2007. It provides native support to Linux-based servers. For further details on it, you can get an informative insight through the KVM guide. IThis guide discusses the core benefits, operational power and functionalities.
KVM vs ESXi: A Quick Comparison
| Feature | KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) | VMware ESXi |
| Type | Type 1 (Integrated into Linux kernel) | Type 1 (Proprietary microkernel) |
| Licensing | Open Source and Free | Proprietary (paid licensing) |
| Management | CLI (virsh) or open-source tools (oVirt, OpenStack) | GUI (vSphere Client, vCenter Server) |
| Ease of Use | Steeper learning curve (requires Linux skills) | Easier (polished GUI and tools) |
| Ecosystem | Strong with Linux/Open Source (e.g., OpenStack) | Mature Enterprise ecosystem (vast integrations) |
| Advanced Features | Requires external platforms (e.g., OpenStack for HA/DRS) | Built-in (vMotion, HA, DRS, Fault Tolerance) |
Why is KVM Important?
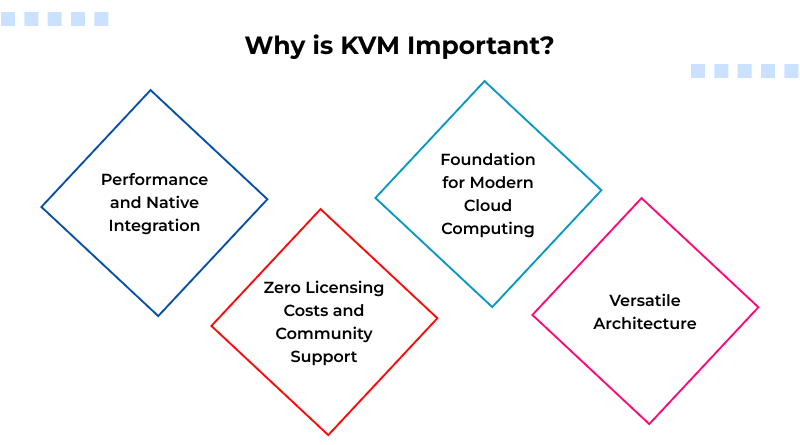
1. Performance and Native Integration
KVM is fully incorporated in the Linux kernel which is in effect converting the kernel to a bare-metal hypervisor. This kind of strong integration allows KVM to take advantage of the powerful features of the Linux operating system, e.g. memory management and security modules, and thus reduce overhead.
By running as a kernel module, KVM directly utilizes hardware virtualization extensions like Intel VT-x and AMD-V. The direct access to underlying hardware tasks like I/O and CPU scheduling gives KVM virtual machines (VMs) near-native performance. Hence, enterprise-grade applications require KVM to operate.
2. Zero Licensing Costs and Community Support
KVM is an open-source technology that is free to use, distribute, and modify. It avoids the significant licensing fees related to proprietary virtualization platforms. It makes it extremely cost-effective for all-sized businesses, from small startups to massive cloud providers.
Its open-source nature encourages a large, active developer community and users who keep adding to its improvements, security updates, and feature development. This leads to quick innovation and flexibility, giving users freedom from vendor lock-in and the chance to tailor the platform to their specific infrastructure needs.
3. Foundation for Modern Cloud Computing
KVM is a key virtualization technology for many private and public cloud platforms. It is part of major open-source cloud frameworks like OpenStack. Its stability and processing power to manage multiple virtual machines make it a popular choice.
It offers necessary tools and APIs for managing vast pools of resources, offering features required for the cloud. KVM facilitates functionalities like live migration, dynamic resource allocation, and advanced network capabilities. KVM’s proven scalability and performance are fundamental to delivering the flexibility and efficiency demanded by today’s cloud infrastructure.
4. Security and Isolation
KVM has a Linux-based feature. It utilizes the robust security architecture. KVM virtual machines are implemented as standard Linux processes. They can be easily isolated and protected using standard Linux security features like SELinux (Security-Enhanced Linux) and cgroups (control groups).
System administrators can implement robust security policies and strict resource limitations for individual VMs. It ensures a strong isolation between virtual environments. This level of security is crucial for multi-tenant environments where protecting one customer’s data from another is paramount.
Why is ESXi Important?
1. Cost Efficiency and Consolidation
ESXi is important because it allows businesses to achieve extreme server consolidation. This replaces the traditional model where each service or application required its own dedicated physical server.
This consolidation leads to lower operating expenses. With fewer physical boxes to power, cool, and store, organizations work with tight IT budgets. The in-house IT team concentrates on managing the virtual environment, making maintenance easier and improving overall cost efficiency.
2. Performance and Stability
ESXi architecture is a Type 1 hypervisor designed for high performance, as it runs directly on the server hardware. This direct access reduces the abstraction layer and overhead that come with running software on a regular operating system. It lets VMs use CPUs, memory, and I/O resources at speeds close to native performance.
If one virtual machine crashes, experiences an operating system error, or is compromised, it will not affect other VMs running on the same physical server..
3. Business Agility and Resilience
ESXi enables the rapid provisioning of computing resources. Instead of waiting days or weeks for a new physical server to be ordered, delivered, and configured, the IT team creates and deploys a functional virtual server from a stored template in a matter of minutes. ESXi facilitates the quick project development to handle sudden traffic spikes in workload demand and accelerates the testing and deployment cycles for new applications.
4. Foundation for Cloud Computing and Automation
ESXi functions in the vSphere ecosystem. It serves as a technical foundation for private and hybrid cloud architectures. Organizations build their internal IaaS offerings by leveraging ESXi clusters. It offers a secured, stable, and isolated virtualized environment required for cloud operations.
By way of its functionalities, IT departments can abstract all computing resources into a programmable and manageable pool and transform hardware into an elastic, utility-like service for internal consumers.
The final note is that you have to evaluate your IT expertise and resources before choosing KVM or ESXi. Understand the desired level of control/flexibility and scalability of the environment. KVM is open-source and free, especially for budget-sensitive organizations for large-scale private clouds where licensing fees for proprietary software would be significant.
ESXi is part of the extended vSphere platform which provides a powerful management interface (vCenter) and functionality that are all seamlessly integrated with one another such as the vMotion, DRS and High Availability. Choose your operational priorities or use our KVM VPS plans to achieve a scalable environment.
FAQs
1. Which hypervisor is generally considered easier to deploy?
VMware ESXi is often thought to be easier to initially deploy to bare metal because of its small footprint and graphical interface, while KVM is more complex to deploy from scratch because it requires more knowledge of the Linux OS for installation and configuration.
2. Which hypervisor is cheaper?
KVM tends to be cheaper, as it is open-source and part of the Linux kernel, meaning there is no cost for the hypervisor itself, compared to the enterprise versions of ESXi.
3. Which hypervisor offers better performance, KVM or ESXi?
Both KVM and ESXi are Type-1 (bare-metal) hypervisors and offer near-native performance, with actual superiority often depending on the specific workload, hardware, and configuration/tuning.
4. Can KVM scale to large, multi-host deployments?
Yes, KVM is highly scalable and is the foundation for many large-scale cloud environments (like OpenStack) and enterprises, but it typically requires additional management tools (like oVirt or OpenStack) for multi-host deployments.