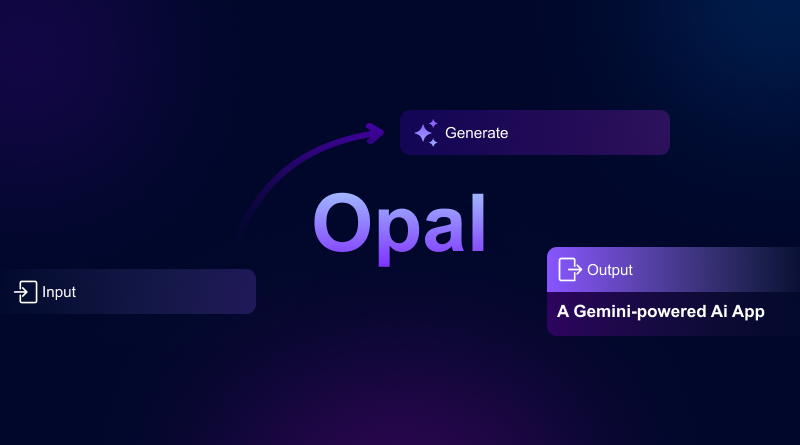
Harnessing the power of the best AI tools has never been an easy task. But they are the one that makes your operational tasks easier. The blog provides insights into the famous Google tool, originally developed in Google Labs. We will understand what Google Opal is. The tool allows you to build and share powerful AI mini-apps that chain prompts and models using simple visual editing.
Google Opal accelerates prototyping AI ideas and workflows. It demonstrates the proof of concept with a functional app. It builds custom AI apps to boost working productivity and more. Let’s take a closer look at this trending AI tool by Google.
Table Of Content
Google Opal: Redefining the Zero Coding Era
Google Opal AI is a zero-coding website-building tool invented by Google. It makes apps complete and usable in a non-conventional way without any coding. The tool like our AI website builder helps simplify workflows, empowering users to build multi-step apps by chaining together prompts, AI model calls, and other tools. Opal requires only one skill-that is the ability to tell the app what you want it to do without coding.
Developers create mini apps using natural language commands. These commands are similar to ChatGPT prompts for website content creation. Google Opal has a visual editor where you can edit or add new features. If you want any further changes, you can describe them in the tool. When the app is finished, it can be shared right away using their personal Google account.
Benefits of Google Opal
1. No-Code / Natural Language App Creation
Google Opal sets no entry barrier for non-coders. It allows them to build AI-powered mini-apps by using prompts. You can easily get started with your personal Gmail account. Non-coders can command a prompt, and Opal translates that into the visual workflow of the app.
It is easier for non-technical users who have automation ideas, task tools, or AI workflows. The operational activity is as similar as n8n. Even n8n eases workflow automation for non-coders. The sky is the limit for innovation as it is not bottlenecked by developers.
2. Visual Workflow Representation & Editing
Opal’s visual representation feature is the best. It converts prompts into a visual workflow that maps I/O (input/output) and AI operations. You can simply drag and drop functionality, making the workflow engaging and the apps intuitive.
Visual clarity is useful for users to see, adjust, or augment each step performed in the backend. It gives transparency and control, making the debugging faster.
3. Rapid Prototyping & Iteration
Opal turns creativity into practical working prototypes. You don’t have to set up an infrastructure, integrate APIs manually, or write boilerplate code. Testing concepts is possible within minutes or hours.
It builds and accelerates feedback cycles to build, test, refine, and repeat. For teams or individuals who want to validate an AI-enabled tool or workflow, Opal allows you to iterate at speed without large upfront investment overhead.
4. Seamless Integration with Google Ecosystem & AI Models
Opal leverages Google’s in-house AI models like Gemini. It also integrates with tools like Google Docs, Sheets, Slides, and more.
The generated outputs already follow the LLM model of Google Apps. It embeds results into the existing workflows or fetches data from Google-powered services. Opal taps into the range of AI capabilities (text, image, video, etc.) that Google supports.
5. Sharing & Remixing of AI Mini-Apps
Apps built on Opal are shareable across devices with a simple link. But these are accessible only for Google account holders to run or modify.
The collaborative or modular model encourages communities to reuse apps. One person creates a useful mini-application; other people modify it to suit their requirements. This could later on result in the development of a pool of applications and templates that could be used by others.
6. Democratization of AI & Empowerment of Non-Developers
Inclusivity is brought about by more involvement and democratization of the app-building workflow. Different ideas and requirements of non-coders scale AI innovation to the next level. Even users from marketing and operations can build customized apps using Opal.
By reducing the technical overhead, Opal works according to creators’ mindsets, and not just consumers. Over time, this could shift organizational dynamics: idea-owners need not always rely on engineering teams to translate their vision into tools.
Use Cases of Google Opal
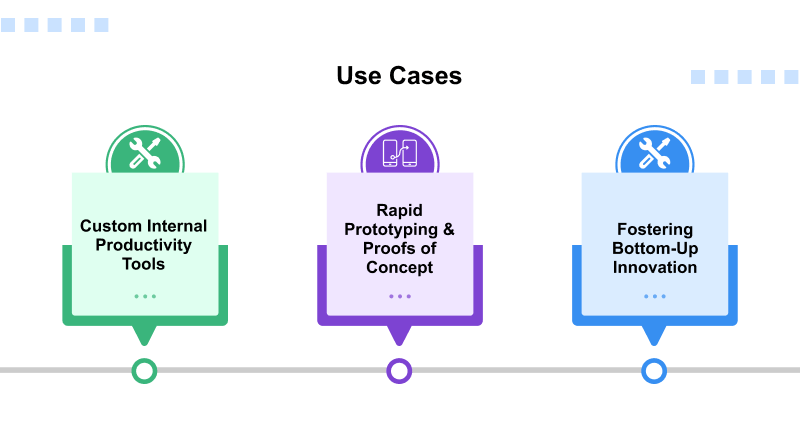
1. Rapid Prototyping & Proofs of Concept (PoCs)
Let’s talk about the Opal’s powerful enterprise use case. Rapid prototyping & PoCs is a manufacturing methodology where product testing is done to check its functionality for users. The new idea or technology before significant investment in full-scale development. So, using Google’s Opal AI, stakeholders can invest in the product demonstration and fund the entire project.
2. Custom Internal Productivity Tools
Build your own mini-app to automate repetitive, domain-specific tasks. This enables employees to solve their own problems without adding to the IT backlog. Using a single product description, a marketing team could generate multiple social media post variations. Or a sales team could create personalized follow-up emails based on meeting notes.
3. Fostering Bottom-Up Innovation
By providing an accessible AI tool to employees across the organization, Opal can be a catalyst for experimentation. It is possible for subject-matter experts to explore AI-powered solutions for their unique challenges, resulting in novel applications that a central IT team might not even dream up on their own.
If you are looking for tangible assets developed by Opal, here are some examples you may refer to.
- Summarizer: Trim long documents, articles, or reports into bullet pointers.
- Support Reply Generator: Drafts professional customer service responses in email and ticket reply formats.
- Copy Enhancer: Edit marketing copies according to the specific brand tone.
- Personal Planner: Generates a daily schedule or to-do list based on a set of tasks and priorities.
How Google Opal Works?
Here is a quick and easy process that proves the simplicity and efficiency of Opal AI.
Describe
Like ChatGPT, you command a prompt in a text box, and perform the same activity here. Describe all functionality and the intention of an application. Example prompt could be:
Prompt:
Act as an expert frontend developer specializing in [React/Angular/HTML/JavaScript].
**GOAL:**
Build a complete, single-page web application for [briefly describe the app’s core purpose, e.g., tracking personal habits, managing project deadlines, or playing a simple game].
**CORE FEATURES (MUST-HAVES):**
1. **State Management:** The application must use [specify state management, e.g., React hooks (useState/useReducer), Angular Signals, or native JS variables] to manage the following data: [list data points, e.g., ‘A list of tasks (text, status)’, ‘Current score’, ‘User input/settings’].
2. **Primary Interaction:** The user must be able to [describe the main action, e.g., ‘Add a new task via an input field and button’, ‘Click a main button to increase the score’, ‘Fetch data from a mock API’].
3. **Data Persistence (If needed):** Use the provided **Firebase Firestore** integration to [describe how data is saved/loaded, e.g., ‘Save the list of tasks’, ‘Store the high score’]. *If you don’t need persistent storage, omit this line.*
**AESTHETICS & UX:**
1. **Styling:** Use Tailwind CSS classes exclusively.
2. **Responsiveness:** The layout must be fully responsive and optimized for both desktop and mobile views.
3. **Look/Feel:** Apply a clean, modern aesthetic with [specify a theme, e.g., ‘dark mode with rounded corners’ or ‘a vibrant, colorful look’].
**CONSTRAINTS (CRITICAL):**
1. **Single File:** All code (HTML structure, CSS styling, and JavaScript/TS logic) **must be in a single file.**
2. **Component:** The primary component must be named `App` and be the default export (for React/Angular).
3. **No External Imports:** Do not use external libraries beyond the core framework and Tailwind CSS (which is pre-loaded).
**OUTPUT:**
Generate the complete, runnable code file named `[AppName].jsx` (or `.html`/`.ts`).
Create
Creating customized apps is the core strength of Opal AI. The user’s prompt is simplified by translating it into a visual workflow graph. The graph is composed of interconnected nodes representing the logical app flow. The visual representation includes an input node, a model call node, and an output node. All these components possess unique functionalities. It makes complex AI processes understandable to a non-tech audience.
Share
Once the setup of the app is completed, the user can publish it instantly. Opal creates a unique web link that can be shared with anyone. Using their Google accounts, other users can then use the mini-app to collaborate and distribute seamlessly.
Google Opal Pricing
The AI tool is available only for US citizens in the beta version. So, the exact pricing and plan features are yet to be decided.
Google Opal AI vs The Competition
| Feature | Google Opal (Experimental Beta) | Workflow Automation Tools (Zapier, Make/n8n) | No-Code App Builders (Bubble, Adalo) |
| Primary Use Case | Building specialized, AI-centric mini-apps by chaining prompts, models, and tools. | Connecting existing software (e.g., Slack, Sheets, CRM) to automate data workflows. | Building full-stack, user-facing web and mobile applications with custom UI/DB. |
| AI Focus | Deep & Integrated: Built specifically for chaining Google’s Gemini models. | Modular: AI is integrated as one step in a wider data flow (often using external APIs like OpenAI). | External: Requires manual connection to external AI APIs for any generative functions. |
| Complexity | Low: Focuses on natural language prompting and simple visual flow. | Medium: Requires understanding API inputs/outputs and complex logical branching. | High: Requires knowledge of database design, UI/UX, and extensive app logic. |
| Pricing | Free (Public Beta) | Paid subscription models based on the number of tasks/operations. | Paid subscription tiers based on features, database size, and web hosting needs. |
| Model Lock-in | High: Restricted to Google’s AI models (Gemini family). | Low: Can choose from various LLMs (GPT-4, Claude, Gemini, etc.). | Low: Can choose from various LLMs via API. |
| Availability | US-only (Beta Phase) | Worldwide | Worldwide |
No need to hold a professional degree to build apps. Google’s Opel AI has penetrated the no-coding market deeply and made app-building accessible to everyone. Regardless of your age, industry, or business size, bring all technical creativity into real life through it. With its free and no-code approach, Opal removes the usual barriers of cost and complexity.
To conclude, Google Opal is not a tool; it is a chance to put creativity into work and implement it into practical applications without the hassle of learning how to write codes. In case you have ever thought of creating your own application, it is a good moment to start with Opal.
FAQs
1. How does Opal use natural language to build applications?
Opal generates a functional, graphical, multi-step workflow based on the natural language descriptions of the desired application functionality, chaining components that include user inputs, AI models (e.g., Gemini), and other tools.
2. Does Google Opal need to know any coding to create applications?
No, Google Opal is a no-code platform where users can build, edit and share AI-based mini-applications using only natural-language instructions and a visual editor.
3. What is the multi-step workflow of Opal?
A multi-step workflow is a visual, structured process of connected steps (or nodes) that make up the overall logical process of the application, i.e., a user input, a search, data manipulated by an AI model, and a resulting output.
4. How does Opal differ from traditional no-code or low-code platforms?
The key difference of Opal is that it focuses on directly turning natural-language prompts into a visual workflow. Hence, making the entire creation process a conversation and obscuring all of the involved logic and snippets of simple code that typically linger in low- or no-code platforms.