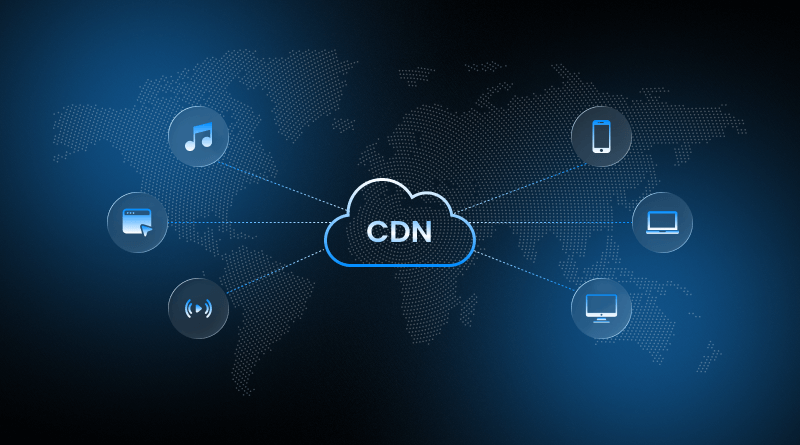
Content distribution and its delivery are major aspects when we discuss web hosting servers. It is a server network that speeds up the loading speed of webpage content. So, whenever you experience minimal latency and optimized bandwidth consumption, give the credit to the CDN. It enhances reliability and performance.
The website loading speed is determined by server location, bandwidth speed, and the data travel time. So, if the user’s machine and the CDN server are nearby, the page loading speed will be low. And vice versa will lead to a higher loading time. For further information, this is the right blog to refer to.
Table Of Content
What is CDN? Explained in a Nutshell
CDN is a globally distributed server network that speeds up the web content delivery to users. The network deploys a caching mechanism that temporarily stores file copies and data centers worldwide. So, whether it is checking your account balance, downloading software instantly, or watching a movie on OTT, it is the CDN network that makes it faster.
CDNs rely heavily on standard HTTP headers to manage caching. Headers like Cache-Control, Expires, and ETag tell the CDN how to handle a specific piece of content, including how long it should be cached (Time-to-Live or TTL), whether it’s public or private, and if it needs to be revalidated with the origin server.
Is a CDN the Same as a Web Host?
A web host server stores the website’s files while CDN is a network of distributed servers caching and delivering the content to users from the closest location. It improves website speed and reliability. Web hosting is the foundation where your site lives, whereas a CDN is a performance and delivery enhancement that optimizes the content’s global distribution.
Latency – How does a CDN improve website load times?
CDN network is helpful for minimal latency in the following ways:
- Using a CDN reduces the distance between users and website resources because it is globally distributed. A CDN lets users connect to a data center that is geographically closer to them instead of the origin server. Faster service means less travel time.
- Optimising hardware and software, such as load balancing and solid-state drives, can speed up data delivery.
- A CDN can reduce data transfer by reducing file sizes using tactics such as minification and compression. Load times are faster when files are smaller.
- By optimizing connection reuse and enabling TLS false starts, CDNs can also speed up sites that use TLS/SSL certificates.
Benefits of CDNs
From supporting core network infrastructure to improving website performance, there are several benefits that CDN offers.
1. Reduce Page Load Time
Faster websites have more traffic and search engine ranking. Web hosting servers with the best CDN networks reduce bounce rates and increase the average time that a user spends on the website. It reduces the loading time by optimizing images, code minification (minification is a process of removing unnecessary characters like whitespace, comments, and line breaks from your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files.)
2. Reduce Bandwidth Costs
You can find that our VPS and dedicated hosting server’s bandwidth costs are competitive. It is because caching and other optimizations by leveraging CDNs reduce the amount of data an origin server must provide. Thus, bandwidth cost is reduced.
3. Increase Content Availability
Network failure and a higher traffic count lead to the website crash. CDN solutions handle more web traffic and reduce the load on web servers. Also, there are operational servers that operate as a backup of multiple CDN servers. It gives a disaster-proof infrastructure to users.
4. Improve Website Security
A DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack generates fake traffic to a website. These are harmful for your website as bot traffic also leads to data breaches. Hence, CDN is there to protect your website by handling such traffic spikes and distributing them across intermediary servers. So, the overall impact on the origin server is reduced.
Examples of CDN
Below, we have shared a few examples of CDN with respective web development frameworks.
– Bootstrap
Bootstrap is a popular front-end framework for developing responsive, mobile-first websites. It relies on both CSS and JavaScript files.
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]/dist/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js"></script>– Font Awesome
Font Awesome provides a large library of scalable vector icons. To use these icons, you include their CSS file via a CDN.
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/font-awesome/6.4.2/css/all.min.css">– React
React is a JavaScript library for building user interfaces.
To use React and React DOM directly in your HTML (for simple projects or prototyping), you can include them via a CDN.
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react@18/umd/react.production.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@18/umd/react-dom.production.min.js"></script>Who Uses CDNs?
From individuals to organizations, a wide range of users use CDNs. Key organizations and online platforms handle traffic surge and deliver content with the minimal latency and higher availability:
- Media and Entertainment: Streaming services like Netflix, JioHotstar, and YouTube use CDNs to deliver video and audio content to millions of users simultaneously, minimizing buffering and latency.
- E-commerce: Online retailers use CDNs to improve site performance, ensure product availability, and maximize business outcomes by providing fast access to their online stores.
- Online Gaming: Gaming companies leverage CDNs to provide low-latency gameplay, fast downloads for game updates, and protection against DDoS attacks, ensuring a seamless experience for players worldwide.
- News and Publishing: News sites use CDNs to deliver articles, images, and multimedia content quickly, even during breaking news events, to keep readers informed and engaged.
CDN Components and Related Technologies
– Domain Name Server
DNS acts as the internet’s directory, mapping domain names and URLs to their respective IP addresses, making it easier for users to access websites without remembering numerical addresses. It simplifies the searching process for specific websites through web browsers. DNS is used by content delivery networks (CDNs) to maintain IP addresses for origin and edge servers and perform dynamic request routing.
– Point of Presence (PoP)
In different regions worldwide, points of presence store servers and routers. Strategically placed in areas of high user density or at intersections of multiple network paths, they ensure optimal connectivity and performance.
– Application Delivery Controller (ADC)
As part of an application delivery network (ADN), an ADC optimizes the delivery of applications over the internet. In addition to improving performance and speed, ADCs can also be used by enterprises operating large-scale, complex, or distributed Content Delivery Networks (CDNs).
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a backbone for modern websites and applications. It allows you to distribute content across any number of servers around the globe, which gives minimal latency, is more reliable, and guarantees a good experience for users. CDNs provide specific technical advantages, such as decreasing page load times, and improving SEO, and offer business benefits.
For companies that exist in a digital-first world, with the users’ expectations shifting to instant access and seamless experiences, the decision to add a CDN has turned into a necessity. If you have a simple blog, an e-commerce business, or an enterprise platform, a good CDN allows you to scale along with ensuring good performance and security.
FAQs
1. How does CDN reduce latency?
As a CDN caches a website’s content in different geographic locations. When a user needs web content, the server closest to them will be available instead of the server far away.
2. How much does CDN improve website speed?
A CDN enhances the speed of the website, and in many cases, it can reduce the page load time especially for the users who are positioned farther away than the hosting server.
3. Does CDN help with SEO?
Yes, a CDN does aid in SEO by speeding up the site (one of the most important ranking factors of search engines such as Google) and improving user experience metrics, such as lower bounce rate and longer dwell time.
4. How do I choose the best CDN provider?
The factors that need to be taken into account to select the best CDN provider include their coverage of the global network, performance and speed, security features, scalability, and pricing model.