“Web 3.0 is about creating a more immersive and interactive web, where users can engage with content in new and dynamic ways.” Mark Zuckerberg, CEO of Facebook
Well said by Mark, that shows the power of the web and immersive technologies in the future. The idea of next-gen web technologies and types of web applications is becoming practical with AR/VR. The evolution of the web world started from Web 1.0>> Web 2.0>>Web 3.0. From the static websites in Web 1.0, to dynamic pages in Web 2.0 are still in the picture. Next, it is Web 3.0, which is a decentralised web that is in progress.
Here is the explainer showing its possibilities, the meaning, and the future.
Table Of Content
What is Web 3.0?
Computer scientist Gavin Wood coined the term Web 3.0 in 2014. It is the next evolution of the World Wide Web. In this, the user interface provides access to documents, applications, and internet multimedia.
In the current stage, Web 3.0 is still in the developing phase. Hence, it hasn’t been accepted universally. Therefore, the proper spelling is also toggling between “Web3” and “Web 3.0.”
Web 3.0 is mainly used in blockchain technological assets like crypto and automatic credit transfer. It will also use machine learning and AI to empower a more intelligent and adaptive web.
Why is Web 3.0 a Trending Topic?
Web 3.0 is the core reason for the paradigm shift in the web world, aiming for a decentralised, user-centric, and secure online experience.
1. Decentralization and User Empowerment
Users have more control over their data, like VPS hosting with Web3 decentralization. In Web 2.0, online platforms have user data control, which restricts their usage to a limited extent.
2. Enhanced Security and Privacy
The blockchain technology in Web 3.0 enhances data security and privacy by integrating more secure and transparent interactions.
3. New Business Models
Web 3.0 opens up opportunities for new business models, particularly in decentralised Autonomous Organisations (DAOs) and peer-to-peer interactions, potentially leading to more inclusive and transparent systems.
4. Technological Advancements
Is Web3 the future? Yes, because it is driving innovation in areas like artificial intelligence (AI), virtual reality (VR), and augmented reality (AR), leading to more immersive and personalized online experiences.
The Evolution: Web 1 vs Web 2 vs Web 3
Let’s go blast from the past when in the late 1980s Tim Berner’s Lee introduced the concept of Web 1. Also, he wrote the HTML (Hypertext Markup Language), which instructs browsers to display content. Web 1 was primarily focused on static information delivery. Hence, in those days, “Hello, World” kind of websites were trending. It had a limited interactive element, read only access, and was created by a small group of developers.
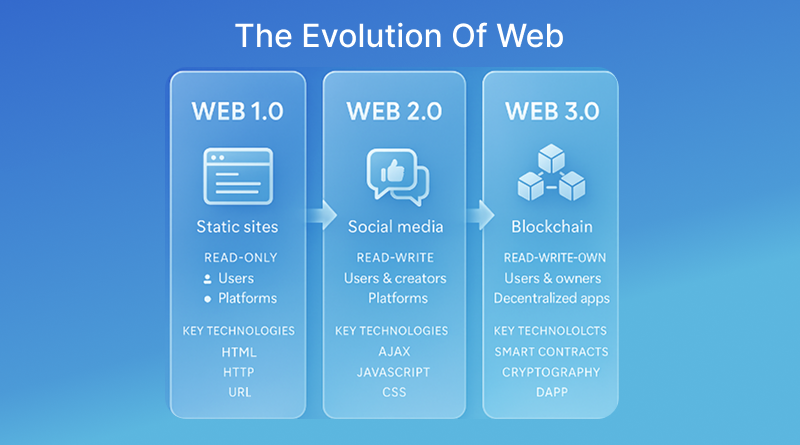
Public awareness of the web increased after the arrival of the Microsoft web browser. Later, it was renamed as Netscape Navigator. In the late 1990s, different browsers like Internet Explorer, and later Apple Safari, or Yahoo, followed the same user-interface pattern. By 2004, Google disrupted the web browsing segment by introducing Google Chrome.
This is when web interactivity was at its peak, calling it Web 2.0. During this era, only Facebook, Orkut, and other social media platforms like YouTube were launched. A Semantic Web standard was released by the World Wide Web Consortium, the web’s standards body. A couple of key Web 3.0 technologies were born at the same time: cryptocurrency and blockchain. Journalists and technologists, including Gavin Wood, co-founder of Ethereum, a prominent blockchain platform, popularized the terms Web 3.0 and Web3 to describe a decentralised, semantically aware web.
| Feature | Web 1.0 | Web 2.0 | Web 3.0 |
| User Experience | “Read-only” web | “Read-write” web | “Read-write-own” web |
| Centralization | Decentralised, but with a few content creators and many passive consumers. | Centralised, with a few large tech companies controlling data and platforms (e.g., Google, Meta, Amazon). | Decentralised, aiming to remove intermediaries and give power back to users. |
| Content Creation | Static content, created by a small number of webmasters and companies. | User-generated content is central (e.g., social media, blogs, wikis). | User-generated content is decentralised and verifiable, with users having ownership over their data and digital assets. |
| Data Ownership | Website owners own data. | Data is owned and controlled by large corporations. Users are the “product.” | Users own and control their own data and digital identity. |
| Core Technologies | HTML, CSS, static pages, and basic scripting. | AJAX, JavaScript frameworks, HTML5, social media platforms, and mobile apps. | Blockchain, peer-to-peer networks, decentralised applications (dApps), smart contracts, AI/Machine Learning. |
| Examples | Personal websites, static directories (e.g., early Yahoo!), informational sites. | Social media (Facebook, Twitter), video streaming (YouTube), e-commerce (Amazon), and cloud services. | Cryptocurrencies, decentralised finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), blockchain-based gaming, decentralised autonomous Organisations (DAOs). |
| Interaction | Minimal interaction. Users primarily browse and consume information. | High interaction and collaboration. Users can comment, share, like, and create content. | Trustless and permissionless interaction. Users can transact and interact with each other without a central authority. |
| Focus | Connecting information. | Connecting people. | Connecting data, people, and things in a meaningful and intelligent way. |
| Monetization | Banner ads and simple advertising. | Targeted advertising, selling user data, and platform subscriptions. | Token-based economies, ownership of digital assets, and direct peer-to-peer transactions. |
Benefits and Challenges of Web 3.0
There is no rose without thorns. Web3 also has pros and cons, which are explained briefly.
Advantages of Web 3.0
1. Data Ownership
Data ownership is in the hands of tech giants like Google, Microsoft, and some government Organisations. The web3 blockchain technology gives the freedom of decentralization, where data ownership is in the end-user’s hands. They have the power to decide what information to share with businesses and advertising firms, and profit.
2. Fewer Intermediaries
Web 3.0 bridges businesses and customers directly using blockchain technology. There will be few or no central authorities receiving a portion of electronic transaction revenues. However, there will be minor regulations and compliance guidelines, but the power of decentralization will result in fewer data intermediaries.
3. Transparency
By using the decentralised web, users will be able to monitor their data and examine the platform’s source code. The parties will always be aware of the value and commerce associated with their relationship. This information can be accessed without an intermediary.
4. Better Marketing
Identifying an individual’s buyer personas is easier because of Web3 technology. Merchants can easily find out the buyer’s requirements. They can sell products or services that buyers are interested in. So, there will be no spam ads.
Disadvantages of Web 3.0
1. Privacy Concerns
Web 3 provides a personalized experience, but privacy threats cannot be ignored. As the web is becoming intelligent and interconnected, it accumulates an increasing amount of user information. Thus, data abuse and privacy violations become easier.
2. Complexity
Advanced skills and expertise are required in Web 3. The talent pool is insufficient to meet the demand for advanced Web 3 applications.
3. Standardization
All Organisations and tech companies follow different data standards. So, web interoperability can be a difficult task.
4. Cost
Due to the use of cutting-edge technologies such as blockchain and artificial intelligence, developing and deploying Web 3.0 applications can be costly.
How Web3 Works?
Let’s break down the principles of how Web3 technology works.
1. Smart Contract
Web3 technology uses smart contracts. These are self-executing digital agreements with terms and conditions built directly into the code and are enforced automatically, without needing a third party like a bank or lawyer.
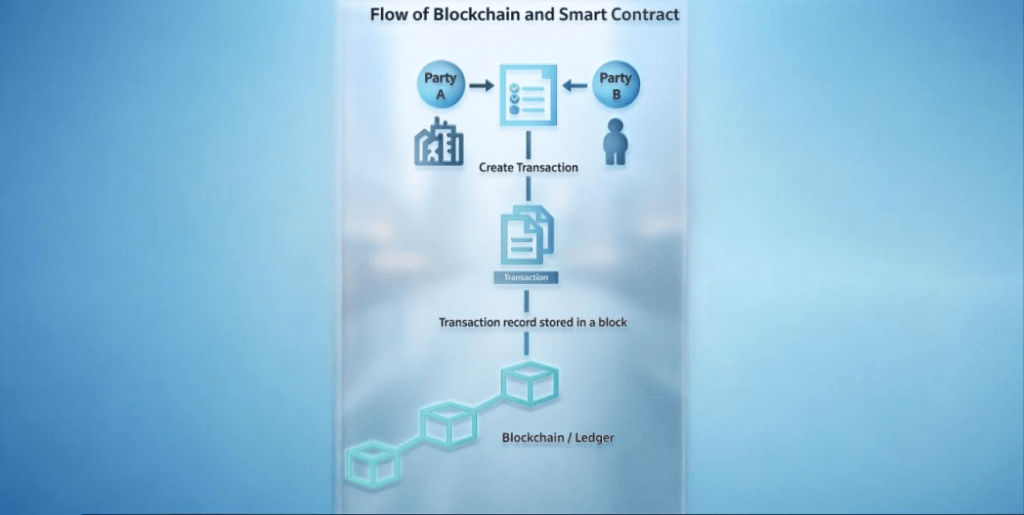
2. User Ownership
Users have 100% ownership of their data and digital assets. Instead of creating an account with a username and password on a company’s server, users interact with dApps using a cryptocurrency wallet.
3. Native Payments and Incentives
Cryptocurrencies play an essential part in the Web3 ecosystem and the networks within them. Users make payments in the form of gas to networks they transact with in cryptocurrencies such as Ether (ETH). Users also utilize Ether when paying fees.
4. Open and Interoperable
Interoperability and open-source software form the foundation of Web3. A lot of Web3 protocols and applications have their code published and serve as a building block for other developers, as well as a trustworthy resource that they can audit for safety. Such openness encourages teamwork and innovation.
Top Web3 Jobs and Career Opportunities
The future of technology is bright. So are the career opportunities in it. Here are the web3 jobs that you can aim for.
- Blockchain Developer
- Blockchain developers design and sustain the underlying infrastructure for Web3 applications. Their responsibilities include working on smart contracts, decentralised apps (dApps), and blockchain protocols such as Ethereum and Solana.
- Smart Contract Auditor
- Auditors actively scan the smart contract’s code for bugs and security breaches. Given the sensitive nature of smart contracts, which control valuable assets, thorough auditing is essential to prevent hacking and ensure safe operations.
- Web3 UX/UI Designer
- Web3 website designers focus on developing easy-to-navigate interfaces for decentralised platforms. Due to the nature of Web3 technology, great UX/UI design is necessary to ensure it is friendly for the average person.
- Community Manager
- Community managers fulfil a crucial function on Web3 projects as they help establish trust and engagement with the user on Discord, Twitter, and Telegram. They are the link from developers to the user and back.
Examples of Web3 Websites and Projects
Web3 websites and projects are characterised by their decentralised nature, often leveraging blockchain technology, cryptocurrencies, and NFTs.
DeFi Platforms
Uniswap
Uniswap is a decentralised exchange that allows users to trade cryptocurrencies without intermediaries.
Aave
Aave is a decentralised lending and borrowing platform where users can earn interest on their crypto assets or take out loans.
Kava
A DeFi platform Kava offers lending, borrowing, and decentralised exchange functionalities according to Hashnode Web3.
Gaming Platforms
Axie Infinity
Axie Infinity is a popular play-to-earn game where players collect, breed, and battle digital pets (NFTs).
The Sandbox
A virtual world in The Sandbox where users can create, own, and monetise their gaming experiences through NFTs.
Infrastructure Projects
Ethereum
A blockchain platform Ethereum enables the development of decentralised applications (dApps) and smart contracts.
Polkadot
Polkadot is a blockchain platform that aims to connect different blockchains, enabling interoperability and scalability.
Is Web3 The Future Of The Internet?
The advent of Web3 has raised the debate of technological decentralization. But we are heading towards it gradually. Unlike today, where a handful of corporations are controlling users’ data, Web3 works on blockchain technology. It enables users to have genuine ownership over their digital assets and data. New economic models like decentralised finance (DeFi) and NFTs are emerging as a result, providing novel ways for people to create, own, and monetize digital content and services.
Hence, Web3 promises a convincing future. But current technological literacy is insufficient to use it for any average person. Several blockchain networks struggle with scalability issues, leading to slow transaction times and high fees. Also, there is no regulation on Web3, which leads to users’ privacy concerns. So, we need to build an ecosystem first, and my take on it is:
“If Web1 gave us information, and Web2 gave us connection, Web3 gives us ownership.”
Web3 is a developing internet innovation that grants power to individuals instead of a single centralized organization, utilizing blockchain, smart contracts, and decentralised applications. Unlike enriched data platforms of Web2, Web3 aims to provide enhanced user privacy, system fairness, actual digital ownership, and user-centric offers. Web3 technology is enabling the pathway towards a more open digital economy, which includes DeFi, NFTs, DAOs, and even a decentralised identity.
Web3 is in a developing stage, but it can redefine the way we communicate, do business, and build trust online. As industries play around with decentralised models, Web3 is set to gain traction, revealing a more precise direction towards the next chapter of the internet. If you are still asking, “What is Web3?”, here is a glimpse of its promise: it can offer a more secure web where users can participate freely, built by the users themselves.
FAQs
When will Web 3.0 be released?
Web3 is not a single product with a set release date, but rather an ongoing evolution of the internet’s infrastructure and principles. Many of its core technologies, like blockchain and decentralised applications (dApps), are already in use and continue to develop, making it a gradual transition rather than an official launch.
Is Web3 active?
Yes, Web3 is actively in development and already in use through various applications and projects. While it is not yet the dominant form of the internet, a growing ecosystem of dApps, cryptocurrencies, and NFTs is built on Web3 principles, with continuous adoption by tech pioneers and a wider audience.
What is web1, web 2 and web3?
Web1 was the “read-only” internet of the 1990s, where content was static and user interaction was minimal. Web2 is the current “read-write” internet, characterized by user-generated content and social media, but controlled by large centralized companies. Web3 is the proposed “read-write-own” internet, a decentralised version where users have ownership and control over their data and digital assets.
Is Google using Web3?
Google is not transitioning its main services to a Web3 model, but its cloud computing division, Google Cloud, is actively supporting the Web3 ecosystem. They provide infrastructure, tools, and resources for developers and businesses to build and scale their decentralised applications and blockchain-based projects.