PostgreSQL is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) that emphasizes extensibility and SQL compliance. Data types are fundamental classifications within programming languages. PostgreSQL has different data types to define the data’s characteristics stored in the database column, serving different purposes. Data modelling, performance optimization, and data integrity are some objectives that can be achieved through PostgreSQL data types. PostgreSQL hosting leverages the native data types is crucial for data modelling, performance optimization, and data integrity.
In this article, we will explore the world of PostgreSQL data types to ease your programming syntax and usage.
Table Of Content
PostgreSQL Data Types: Understanding the Basics
PostgreSQL specifies what type of data can be stored in any particular table column, function argument, or variable. It is important to understand data types for data integrity, storage efficiency, and query performance. Let us illustrate this with an example.
For example, if the column holds a “Whole Number” (like INTEGER), then the column will accept only numbers and no words like “website.” For text, you need to add the VARCHAR data type, where you can put names, characters, sentences, or addresses.
PostgreSQL Data Types with Examples
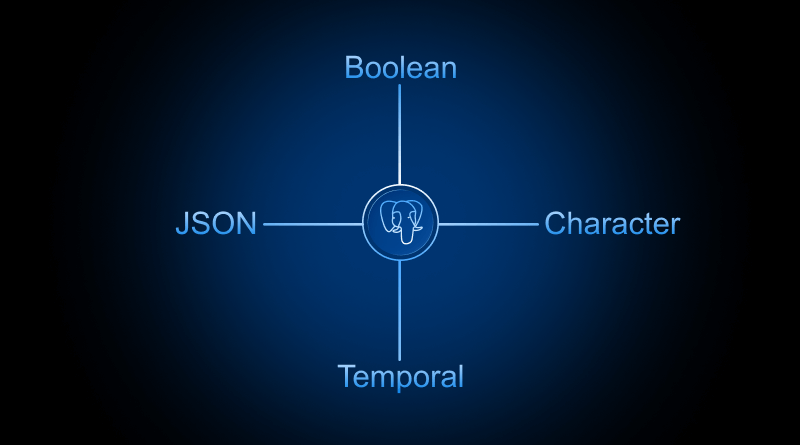
Step-by-step we will explore the different PostgreSQL data types with examples. Numeric, character, Boolean, array, and more are types that help web developers.
PostgreSQL Numeric Data Types
Integer Data Types
SMALLINT and INTEGER are two commonly used data types. SMALLINT is a 2-byte signed integer, with a range of -32768 to +32767. INTEGER is a 4-byte signed integer, with a range of -2147483648 to +2147483647.
Example:
CREATE TABLE employees (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT,
age INTEGER,
salary NUMERIC(10, 2)
);Decimal Data Types
NUMERIC and DECIMAL are two decimal data types used to store numbers with the fixed digit. The difference between the two types is that DECIMAL is an alias for NUMERIC, but with different default precision and scale values.
Example:
CREATE TABLE orders (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
customer TEXT,
amount NUMERIC(10, 2)
);PostgreSQL Character Data Types
Char Data Type
The char data type stores fixed-length character strings. When defining a column with the char data type, you need to specify the string length. For example, to create a table with a column named “last_name” of type char(20):
Example:
CREATE TABLE employees (
employee_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
last_name char(20),
first_name varchar(20),
hire_date date
);Text Data Type
The PostgreSQL data type stores long text strings with a limited specified length. For instance, to create a table with a column named “description” of type text:
CREATE TABLE products (
product_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
product_name varchar(50),
description text,
price decimal(8,2)
);PostgreSQL Date/Time Data Types
Date Data Type
The date data type stores dates in the format YYYY-MM-DD. To create a table with a column named “order_date” of type date, for example:
CREATE TABLE orders (
order_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
order_date date,
customer_id int,
product_id int,
quantity int,
total decimal(8,2)
);Time Data Type
In the time data type, the time is stored as HH:MI:SS. To create a table with a column named “checkin_time” of type time, for example:
CREATE TABLE visitors (
visitor_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
first_name varchar(20),
last_name varchar(20),
check-in time,
checkout time
);PostgreSQL Boolean Data Type
There are only two possible values for this data type: TRUE or FALSE. A flag’s state, or the result of a logical operation, can be represented by only two states, making it useful in many situations.
A table with a Boolean column looks like this:
CREATE TABLE orders (
order_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
customer_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
order_date DATE NOT NULL,
shipped BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE
);The “shipped” column has a default value of FALSE in this example.
PostgreSQL Composite Data Types
The composite data type allows you to define your own data types by combining multiple data types. You can use this when you need to store multiple related values in a single column.
An example of a composite data type is as follows:
CREATE TYPE address AS (
street VARCHAR(50),
city VARCHAR(50),
state CHAR(2),
zip VARCHAR(10)
);This example defines a new data type called “address” that consists of four fields: street, city, state, and zip.
This data type can then be used in a table definition as follows:
CREATE TABLE customers (
customer_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
address address
);The custom composite data type “address” is used in this example for the “address” column.
PostgreSQL Array Data Type
You can store multiple values of the same data type in a single column using the data type array. You can use this to store a list of values, such as phone numbers or e-mail addresses.
An array column in a table looks like this:
CREATE TABLE users (
user_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
emails TEXT[] NOT NULL
);This column is of type TEXT[] (an array of text values).
An array data type can be used to store a list of email addresses for a user. As an array, you can store all the email addresses instead of creating separate rows for each one.
PostgreSQL is remarkable for its rich and flexible array of data types, which allow the developer to accurately model the data with efficiency. From simple data types such as integers, text, and Boolean to more sophisticated types such as JSON, arrays, and geometry or network types, PostgreSQL will perform efficiently and quickly at scale and can be applied to many use cases.
Regardless of if you’re creating a basic web app or a more complex enterprise standard system, knowing the appropriate PostgreSQL data types will help you compact and retrieve data effectively, maximizing your use of the database not just as a data storage mechanism, but as an innovative framework for use in solutions.
FAQs
1. What are the main categories of PostgreSQL data types?
PostgreSQL has primarily defined nine data types: numeric, character, date/time, boolean, geometric, network, JSON, array, and user-defined types, giving users great diversity in data handling.
2. Does PostgreSQL support JSON data types?
Yes, PostgreSQL has both JSON and JSONB data types, and you can use them to efficiently store, query, and manipulate structured JSON data.
3. What are the basic data types available in PostgreSQL?
Some of the basic data types in PostgreSQL include Integer, Decimal, Boolean, Character (char, varchar, text), and Date/Time types for basic data operations.
4. What are the main data types in PostgreSQL?
The principal data types in PostgreSQL include numeric, character, Boolean, date/time, JSON, array, and geometric data types for specific data storage and processing.